The letter was aimed at Mark Zuckerberg, Facebook’s chief executive, and his top lieutenants. It decried the social network’s recent decision to let politicians post any claims they wanted — even false ones — in ads on the site. It asked Facebook’s leaders to rethink the stance.
The message was writt by Facebook’s own employees.
Facebook’s position on political advertising is “a threat to what FB stands for,” the employees wrote in the letter, which was obtained by The New York Times. “We strongly object to this policy as it stands.”
For the last two weeks, the text of the letter has been publicly visible on Facebook Workplace, a software programme that the Silicon Valley company uses to communicate internally. More than 250 employees have signed the message, according to three people who have seen it and who declined to be identified for fear of retaliation.
While the number of signatures on the letter was a fraction of Facebook’s 35,000-plus workforce, it was one sign of the resistance that the company is now facing internally over how it treats political ads.
Many employees have been discussing Zuckerberg’s decision to let politicians post anything they want in Facebook ads because those ads can go viral and spread misinformation widely. The worker dissatisfaction has spilled out across winding, heated threads on Facebook Workplace, the people said.
For weeks, Facebook has been under attack by presidential candidates, lawmakers and civil rights groups over its position on political ads. But the employee actions — which are a rare moment of internal strife for the company — show that even some of its own workers are not convinced the political ads policy is sound. The dissent is adding to Facebook’s woes as it heads into the 2020 presidential election season.
“Facebook’s culture is built on openness, so we appreciate our employees voicing their thoughts on this important topic,” Bertie Thomson, a Facebook spokeswoman, said in a statement. “We remain committed to not censoring political speech and will continue exploring additional steps we can take to bring increased transparency to political ads.”
Facebook has been struggling to respond to misinformation on its site since the 2016 presidential election, when Russians used the social network to spread inflammatory and divisive messages to influence the US electorate. Zuckerberg has since appointed tens of thousands of people to work on platform security and to deter coordinated disinformation efforts.
But figuring out what is and isn’t allowed on the social network is slippery. And last month, Facebook announced that politicians and their campaigns would have nearly free rein over content they post there. Previously, the company had prohibited the use of paid political ads that “include claims debunked by third-party fact checkers.”
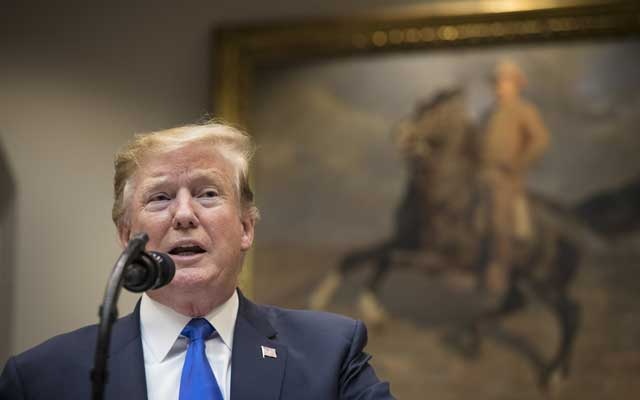
This month, President Donald Trump’s campaign began circulating an ad on Facebook that made false claims about former Vice President Joe Biden, who is running for president. When Biden’s campaign asked Facebook to remove the ad, the company refused, saying ads from politicians were newsworthy and important for discourse.
Sen. Elizabeth Warren, D-Mass., who is also running for president, soon took Facebook to task. She bought a political ad on Facebook that falsely claimed Zuckerberg and his company supported Trump for president. Neither Zuckerberg nor Facebook have endorsed a political candidate.
Warren said she wanted to see how far she could take it on the site. Zuckerberg had turned his company into a “disinformation-for-profit machine,” she said.
But Zuckerberg doubled down. In a 5,000-word speech to students at Georgetown University in Washington this month, the chief executive defended his treatment of political ads by citing freedom of expression. He said Facebook’s policies would be seen positively in the long run, especially when compared with policies in countries like China, where the government suppresses online speech.
“People having the power to express themselves at scale is a new kind of force in the world — a fifth estate alongside the other power structures of society,” Zuckerberg said at the time.
Zuckerberg also said Facebook’s policies were largely in line with what other social networks — like YouTube and Twitter — and most television broadcasters had decided to run on their networks. Federal law mandates that broadcast networks cannot censor political ads from candidates running for office.
Inside Facebook, Zuckerberg’s decision to be hands off on political ads has supporters. But dissenters said Facebook was not doing enough to check the lies from spreading across the platform.
While internal debate is not uncommon at the social network, it historically has seen less internal turmoil than other tech companies because of a strong sense of mission among its rank-and-file workers.
That has set it apart from Google and Amazon, which for the last few years have grappled with several employee uprisings. Most notably, 20,000 Google workers walked off the job in 2018 to protest the company’s massive payouts to executives accused of sexual harassment.
Last week, Google employees again challenged management over new software that some staff said was a surveillance tool to keep tabs on workplace dissent. At an employee meeting Thursday, Sundar Pichai, Google’s chief executive, said he was working on ways to improve trust with employees, while acknowledging it was challenging to maintain transparency as the company grows. A video of Pichai’s comments was leaked to The Washington Post.
Amazon has faced employee pressure for nearly a year to do more to address the company’s effect on climate change. Some employees worked on a shareholder resolution to push the company on the matter, and more than 7,500 Amazon workers publicly signed a letter to support the proposal. In September, Jeff Bezos, Amazon’s chief executive, announced the company was accelerating its climate goals, aiming to be carbon neutral by 2040.
In the Facebook employee letter to Zuckerberg and other executives, the workers said the policy change on political advertising “doesn’t protect voices, but instead allows politicians to weaponize our platform by targeting people who believe that content posted by political figures is trustworthy.”
It added, “We want to work with our leadership to develop better solutions that both protect our business and the people who use our products.”
The letter then laid out product changes and other actions that Facebook could take to reduce the harm from false claims in advertising from politicians. Among the proposals: changing the visual design treatment for political ads, restricting some of the options for targeting users with those ads and instituting spending caps for individual politicians.
“This is still our company,” the letter concluded.